
You are now leaving GSK’s website and are going to a website that is not operated/controlled by GSK. Though we feel it could be useful to you,we are not responsible for the content/service or availability of linked sites. You are therefore mindful of these risks and have decided to go ahead.
Agree Agree Agree Stay
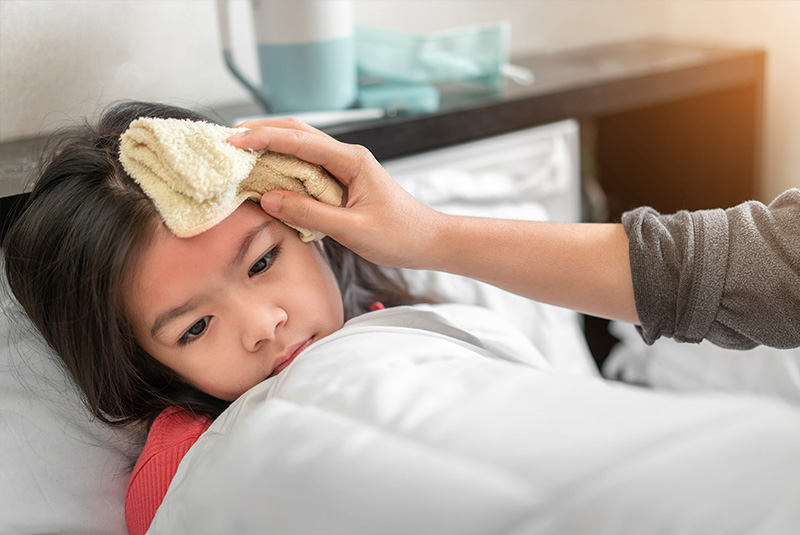
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a common respiratory illness that can be particularly severe for infants and young children 1. Their still-developing immune systems make them more vulnerable to complications, which can lead to serious health issues like pneumonia, hospitalisations, or even death 1. In fact, each year, around 20,000 children under the age of 5 are hospitalised due to complications from the influenza disease 2.
As a parent, it’s essential to be aware of these risks and take proactive measures to protect your child's health. This blog will offer valuable information on influenza disease, including its risks and prevention measures, to help you keep your child safe and well.
Influenza is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses 1,3. It primarily affects the nose, throat, and lungs, and can be particularly challenging for infants and young children due to their immature immune systems 3.
Children under 5 years old, especially those under 2 years old and those with certain chronic health conditions, face a higher risk of severe flu complications 4. This includes 4:
Flu viruses are of four types: A, B, C, and D. Influenza A and B are the main causes of seasonal flu epidemics 1,3. These viruses spread rapidly through droplets released into the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Others can then inhale these viral droplets and become infected. The virus can also be transmitted via hands that have touched infected droplets or contaminated surfaces 1.
Young children are especially susceptible to influenza due to frequent interactions in crowded settings like schools and nursing homes 1.
Vaccination is a key preventive measure against influenza. The influenza vaccination is safe and helps strengthen the immune system to fight the virus effectively, reducing the risk of infection and its spread 5.
Influenza symptoms typically begin about 2 days after exposure to the virus, but they can appear anywhere from 1 to 4 days later 1. These symptoms can vary from mild to severe and usually appear suddenly 6. Common influenza symptoms include 6,1:
Children may also experience vomiting and diarrhoea 5. The cough associated with the flu can be severe and may last for 2 weeks or longer 1. Most people recover from the flu within a few days to less than two weeks 6.
In children, severe influenza-related symptoms that require medical attention may include 6:
Children may also experience complications that can be life-threatening and potentially fatal, including 6:
Influenza vaccinations help lower the number of flu cases, hospital visits, and deaths each year 5.
Influenza vaccination is a key measure to protect your child from the flu 5. The vaccination is recommended annually for children aged 6 months and older and stimulates the immune system to recognise and combat the influenza virus, reducing the chances of severe illness 5,7.
Vaccinating children is vital as it prevents flu-related illnesses, minimises doctor visits and hospitalisations, and lowers the risk of severe symptoms, ICU care, and flu-related deaths. It is particularly important for children with chronic health conditions, as it helps manage these conditions and reduce the risk of complications 8.
As parents, you may want to consider the 7-Star Protection Programme, a comprehensive vaccination schedule created by the IAP Advisory Committee on Vaccination & Immunization Practices (ACVIP). This programme includes influenza vaccination and protection against other significant diseases such as Hepatitis A, Chickenpox, Mumps, Meningitis, and Rubella.
Consult your paediatrician to learn more about the 7-Star Protection schedule.
Along with vaccination, parents can take additional measures to help reduce the spread of influenza viruses 1,5:
Conclusion
Preventing influenza disease in infants and young children is vital due to their higher risk of severe complications 1,6. By understanding these risks, ensuring annual vaccinations, and following practical prevention measures, you can help lower the chances of your child contracting the flu and experiencing its harmful effects 5.
Influenza vaccination is a key strategy for flu prevention, helping to reduce the incidence of illnesses, hospitalisations, and deaths each year 5.
Consult your paediatrician for advice and to ensure your child receives the essential vaccinations and care.
References
