
You are now leaving GSK’s website and are going to a website that is not operated/controlled by GSK. Though we feel it could be useful to you,we are not responsible for the content/service or availability of linked sites. You are therefore mindful of these risks and have decided to go ahead.
Agree Agree Agree Stay
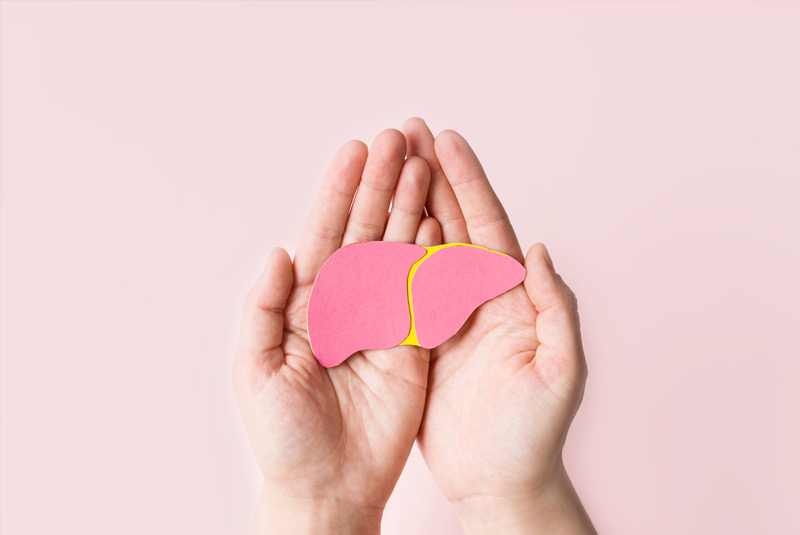
Hepatitis A is a contagious liver infection which is caused by the Hepatitis A virus. Its severity can range from a mild to severe illness which can last from few weeks to months.1
The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that globally more than 10 crore people get infected with Hepatitis A every year. While this liver infection is generally considered mild and common among children, it can be serious in some cases.1 Among older children and adults, infection usually causes more severe symptoms, jaundice being one of them occurring in more than 70% of cases.2
Hepatitis A infections do not cause chronic infections; however, they can be severe. If left unchecked, in some cases, it can lead to severe complications like acute liver failure and death in rare cases. Outbreaks occur worldwide, especially in areas with poor sanitation. This is why children, who are not previously exposed to this virus because of living in more hygienic urban areas, may evade Hepatitis A infection in early childhood leaving them at risk of severe infection in adolescence and adulthood.1
Hepatitis A spreads through ingestion of water and food contaminated with Hepatitis A virus. It is primarily transmitted from person to person by the faecal-oral route or when someone ingests contaminated water, milk, or even foods that have not been prepared, stored, or served in a hygienic manner.1
You are at risk of contracting Hepatitis A if you accidentally ingest something contaminated with Hepatitis A, like changing an infected child’s diaper and not washing your hands thoroughly after. You are even at risk if you share food and drinks at a restaurant or touch a door-knob or surface that might have some undetected amounts of stool from an infected person.1
Not everyone who is infected has symptoms. Symptoms (if developed) usually appear within 2 to 6 weeks after infection. They can include3:
Remember, not everyone who is infected will show all the symptoms. In few cases, symptoms can last for as long as 6 months.3
Yes, Hepatitis A infection can be prevented. The easiest ways to protect yourself are to1:
There is no specific treatment for Hepatitis A hence it is wise to prevent the disease by taking preventive measures. Vaccination is a reliable way to prevent Hepatitis A.1
Vaccination against Hepatitis A can be given to children aged one year and above. This is why, global, and national health authorities like WHO and Indian Academy of Pediatrics recommend Hepatitis A vaccination to all eligible children.1,4 Consult your Paediatrician for more information.
Ensuring your child's health is crucial, and 7-Star Protection offers protection through seven essential vaccinations. One of these vaccinations protects against Hepatitis A, a contagious liver infection particularly harmful to young children. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain, potentially leading to serious complications.
Vaccinating your child early can prevent Hepatitis A and its associated issues. With 7-Star Protection, your child is protected against Hepatitis A and other serious diseases, promoting a healthy and happy childhood.
References:
